启动模式
react启动的模式
react有3种模式进入主体函数的入口,从 react官方文档 使用 Concurrent 模式(实验性)中对比三种模式:
- legacy 模式:
ReactDOM.render(<App />, rootNode)。这是当前 React app 使用的方式。当前没有计划删除本模式,但是这个模式可能不支持一些新功能。 - blocking 模式:
ReactDOM.createBlockingRoot(rootNode).render(<App />)。目前正在实验中。作为迁移到 concurrent 模式的第一个步骤。 - concurrent 模式:
ReactDOM.createRoot(rootNode).render(<App />)。目前在实验中,未来稳定之后,打算作为 React 的默认开发模式。这个模式开启了所有的新功能。

legacy 模式在合成事件中有自动批处理的功能,但仅限于一个浏览器任务。非 React 事件想使用这个功能必须使用 unstable_batchedUpdates 。在 blocking 模式和 concurrent 模式下,所有的 setState 在默认情况下都是批处理的。会在开发中发出警告
不同模式在react运行时的含义
legacy模式是我们常用的,它构建dom的过程是同步的,所以在render的reconciler中,如果diff的过程特别耗时,那么导致的结果就是js一直阻塞高优先级的任务(例如用户的点击事件),表现为页面的卡顿,无法响应。
concurrent Mode是react未来的模式,它用时间片调度实现了异步可中断的任务,根据设备性能的不同,时间片的长度也不一样,在每个时间片中,如果任务到了过期时间,就会主动让出线程给高优先级的任务。详见scheduler&lane模型 。
两种模式函数主要执行过程
1. 主要执行流程:

2.详细函数调用过程:
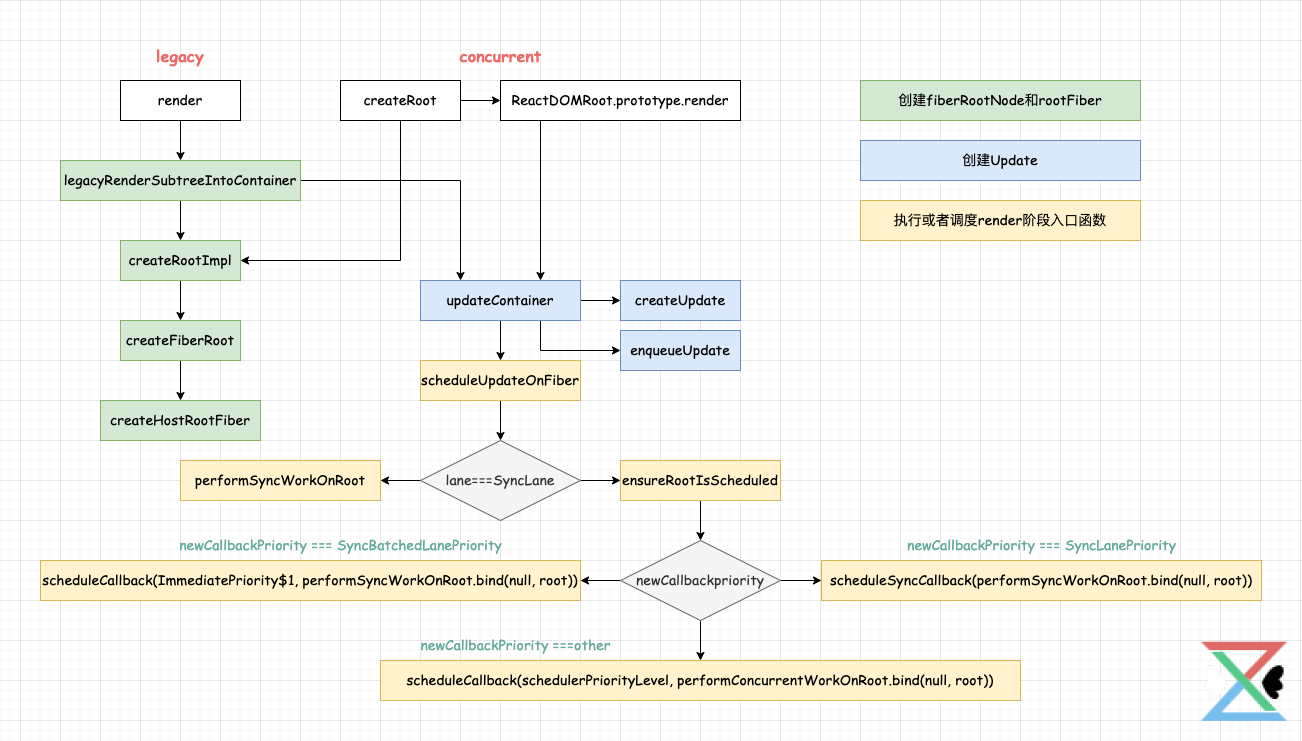
3.legacy模式:
- render调用legacyRenderSubtreeIntoContainer,最后createRootImpl会调用到createFiberRoot创建fiberRootNode, 然后调用createHostRootFiber创建rootFiber,其中fiberRootNode是整个项目的的根节点,rootFiber是当前应用挂在的节点,也就是ReactDOM.render调用后的根节点
//最上层的节点是整个项目的根节点fiberRootNode
ReactDOM.render( < App / > , document.getElementById("root")); //rootFiber
ReactDOM.render( < App / > , document.getElementById("root")); //rootFiber

- 创建完Fiber节点后,legacyRenderSubtreeIntoContainer调用updateContainer创建创建Update对象挂载到updateQueue的环形链表上,然后执行scheduleUpdateOnFiber调用performSyncWorkOnRoot进入render阶段和commit阶段
4.concurrent模式:
- createRoot调用createRootImpl创建fiberRootNode和rootNode
- 创建完Fiber节点后,调用ReactDOMRoot.prototype.render执行updateContainer,然后scheduleUpdateOnFiber异步调度performConcurrentWorkOnRoot进入render阶段和commit阶段
5.legacy模式主要函数注释
function legacyRenderSubtreeIntoContainer(parentComponent, children, container, forceHydrate, callback) {
//...
var root = container._reactRootContainer;
var fiberRoot;
if (!root) {
// mount时
root = container._reactRootContainer = legacyCreateRootFromDOMContainer(container, forceHydrate); //创建root节点
fiberRoot = root._internalRoot;
if (typeof callback === 'function') { //处理回调
var originalCallback = callback;
callback = function() {
var instance = getPublicRootInstance(fiberRoot);
originalCallback.call(instance);
};
}
unbatchedUpdates(function() {
updateContainer(children, fiberRoot, parentComponent, callback); //创建update入口
});
} else {
// update时
fiberRoot = root._internalRoot;
if (typeof callback === 'function') { //处理回调
var _originalCallback = callback;
callback = function() {
var instance = getPublicRootInstance(fiberRoot);
_originalCallback.call(instance);
};
}
updateContainer(children, fiberRoot, parentComponent, callback);
}
}
function createFiberRoot(containerInfo, tag, hydrate, hydrationCallbacks) {
var root = new FiberRootNode(containerInfo, tag, hydrate); //创建fiberRootNode
const uninitializedFiber = createHostRootFiber(tag); //创建rootFiber
//rootFiber和fiberRootNode连接
root.current = uninitializedFiber;
uninitializedFiber.stateNode = root;
//创建updateQueue
initializeUpdateQueue(uninitializedFiber);
return root;
}
//对于HostRoot或者ClassComponent会使用initializeUpdateQueue创建updateQueue,然后将updateQueue挂载到fiber节点上
export function initializeUpdateQueue < State > (fiber: Fiber): void {
const queue: UpdateQueue < State > = {
baseState: fiber.memoizedState, //初始state,后面会基于这个state,根据Update计算新的state
firstBaseUpdate: null, //Update形成的链表的头
lastBaseUpdate: null, //Update形成的链表的尾
//新产生的update会以单向环状链表保存在shared.pending上,计算state的时候会剪开这个环状链表,并且连接在lastBaseUpdate后
shared: {
pending: null,
},
effects: null,
};
fiber.updateQueue = queue;
}
function updateContainer(element, container, parentComponent, callback) {
var lane = requestUpdateLane(current$1); //获取当前可用lane
var update = createUpdate(eventTime, lane); //创建update
update.payload = {
element: element //jsx
};
enqueueUpdate(current$1, update); //update入队
scheduleUpdateOnFiber(current$1, lane, eventTime); //调度update
return lane;
}
function scheduleUpdateOnFiber(fiber, lane, eventTime) {
if (lane === SyncLane) { //同步lane 对应legacy模式
//...
performSyncWorkOnRoot(root); //render阶段的起点 render在第6章讲解
} else { //concurrent模式
//...
ensureRootIsScheduled(root, eventTime); //确保root被调度
}
}
6.concurrent主要函数注释:
function ensureRootIsScheduled(root, currentTime) {
//...
var nextLanes = getNextLanes(root, root === workInProgressRoot ? workInProgressRootRenderLanes : NoLanes); //计算nextLanes
//...
//将lane的优先级转换成schduler的优先级
var schedulerPriorityLevel = lanePriorityToSchedulerPriority(newCallbackPriority);
//以schedulerPriorityLevel的优先级执行performConcurrentWorkOnRoot 也就是concurrent模式的起点
newCallbackNode = scheduleCallback(schedulerPriorityLevel, performConcurrentWorkOnRoot.bind(null, root));
}
7. 两种模式的不同点:
- createRootImpl中传入的第二个参数不一样 一个是LegacyRoot一个是ConcurrentRoot
- requestUpdateLane中获取的lane的优先级不同
- 在函数scheduleUpdateOnFiber中根据不同优先级进入不同分支,legacy模式进入performSyncWorkOnRoot,concurrent模式会异步调度performConcurrentWorkOnRoot